How to use the Data Query Playground
This short guide will show you how to use the Data Query Playground application for exploring the DHIS2 Web API and for testing data queries and mutations.
What is the Query Playground?
The Data Query Playground is a DHIS2 application that was built to facilitate the development of your application especially when talking to the DHIS2 Web API through the DHIS2 App Runtime.
The Query Playground makes it easy to test different REST API requests and to help you define or experiment writing queries, whether it's for fetching data or mutating data (making POST, PUT or DELETE requests - in the App Runtime these equals to create, update, and delete).
How to access it?
Through the App Runtime Documentation. When you go to the App Runtime documentation, you will see a big blue button on the sidebar on the left:
How to use it?
When you get to the sign-in page, you will need to enter your existing DHIS2 instance URL as the server as well as username and password.
Once you're signed in, you'll see the following homepage:
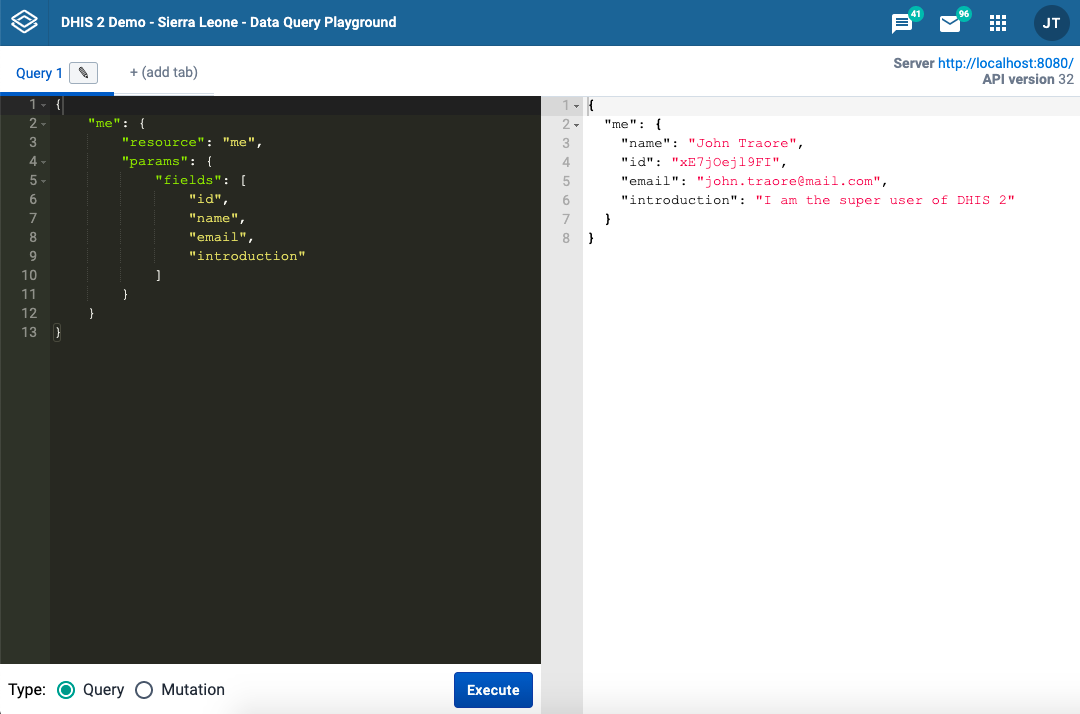
On the left, you have the definition of a query that you want to execute, and on the right, you will get the response for that API request.
At the bottom of the query definition section you'll see the options Query and Mutation and the button Execute.
Data Query
In the example above, we're getting the response of the default data query object which is the resource me and it's providing the user details.
A resource is a type of object that you want to request from the API - we can test other resources such as indicators, programs, etc.
In this example, we want to fetch the first 3 programs in the system. Feel free to run this query and check the response:
{
"results": {
"resource": "programs",
"params": {
"pageSize": 3,
"fields": ["id", "displayName"]
}
}
}
This application uses JSON syntax which requires double quotes to be used around strings and property names.
Data Mutation
To test data mutations you can easily do this by defining the type of mutation that you want to execute. You can specify a type as create, update or delete.
Create
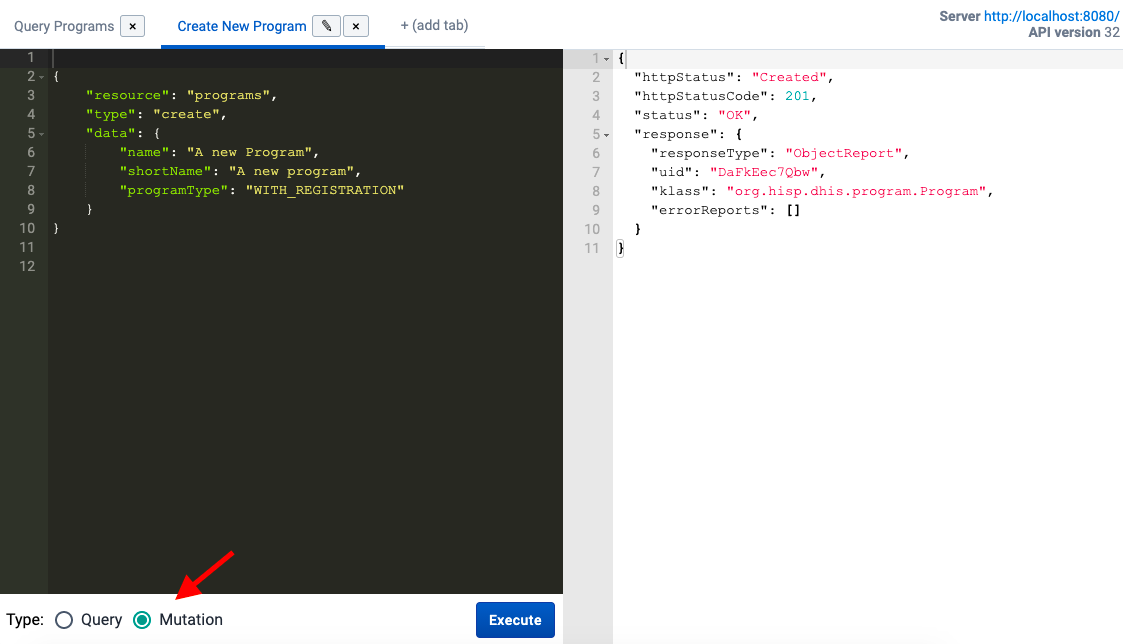
In the example below, we're creating a new program. Notice that the data property is required in type create (as well as for type update - see next section).
{
"resource": "programs",
"type": "create",
"data": {
"name": "A new Program",
"shortName": "A new Program",
"programType": "WITH_REGISTRATION"
}
}
Before running this request, we select the Mutation option and click Execute. See the results on the left:
Useful keyboard shortcut: You can also execute Query and Mutation without a mouse by pressing Ctrl+Enter ⚡️
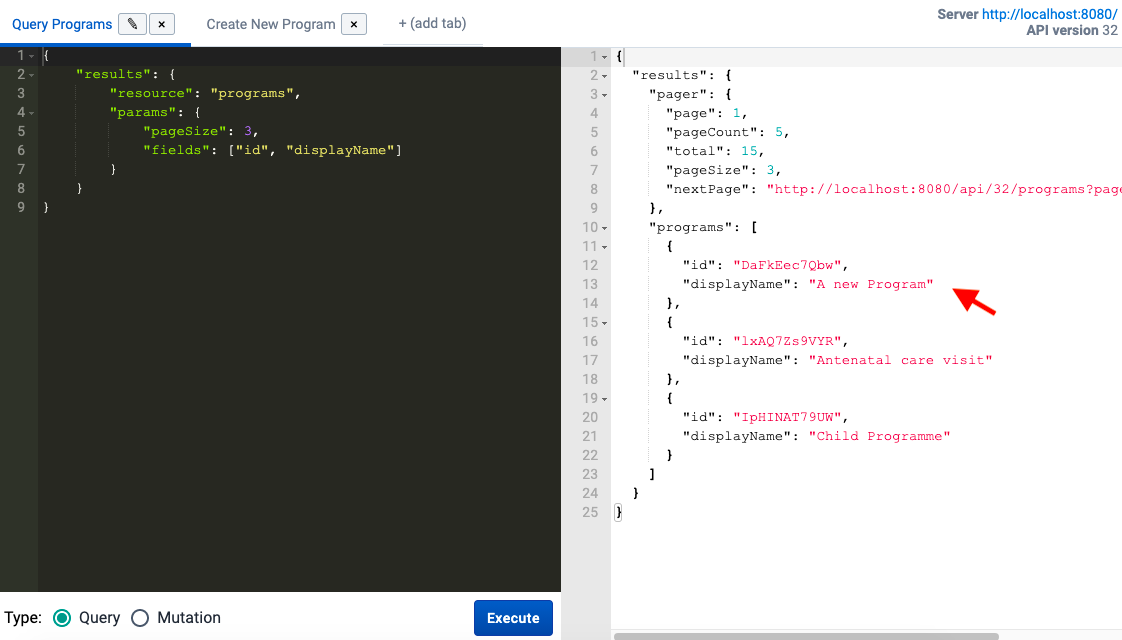
After we've created a new program, we can verify the result of this action by going back to the programs query and executing it again to see the response - as you can see, "A new Program" was successfully added:
Update
For update and delete types, the id property is required. See the query definition examples below:
{
"resource": "programs",
"type": "update",
"id": "DaFkEec7Qbw",
"data": {
"name": "A program - Updated",
"shortName": "A program - Updated",
"programType": "WITH_REGISTRATION"
}
}
Delete
{
"resource": "programs",
"type": "delete",
"id": "DaFkEec7Qbw"
}
Want to learn more?
- You can find more examples of data mutations on the App Runtime documentation here.
- Check this short video from the Developer Academy 2021 to learn more about using the Data Query Playground.